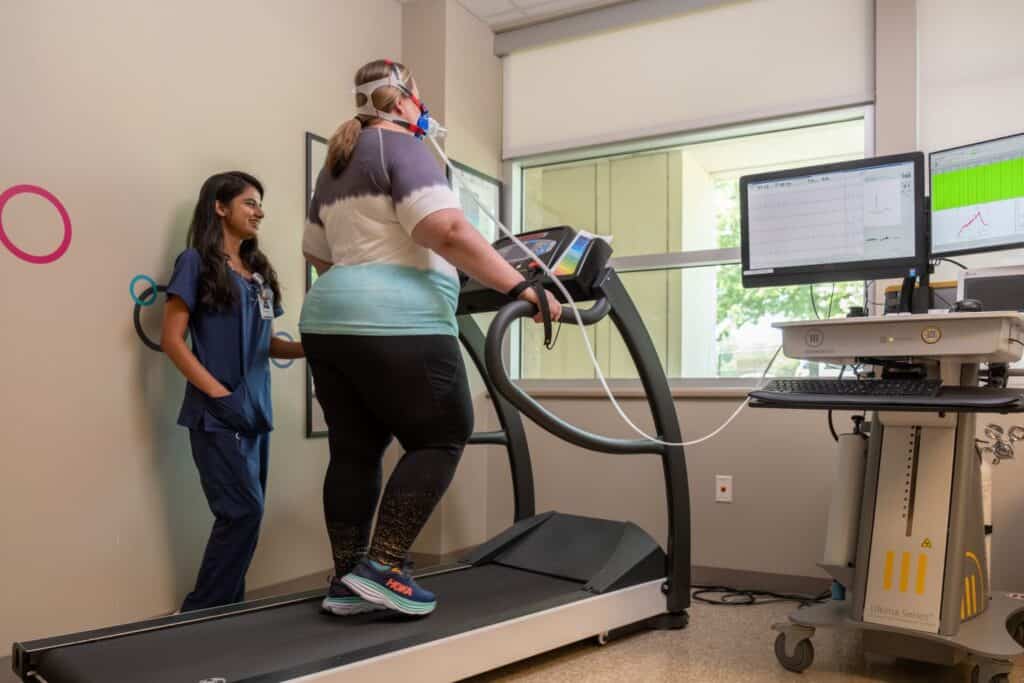
Center investigators Drs. Eva C. Diaz, Xiawei Ou, Elisabet Børsheim, were part of a team that recently published results from a 4-week RCT examining the effects of short-term supervised exercise training on liver fat in adolescents with obesity. The supervised exercise [high-intensity interval training (HIIT)] had beneficial effects on markers of cardiometabolic health, and after limiting analysis to participants with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, HIIT decreased intrahepatic triglyceride content. A reduction of liver fat was insignificant in participants with varying degrees of liver fat at baseline. This supports evidence that HIIT is a safe and efficient exercise that can be prescribed for the treatment of metabolic complications of obesity in adolescent – though additional research is needed to optimize HIIT protocols for greatest cardiometabolic health benefit.